Deactivate Data Pipeline Architecture
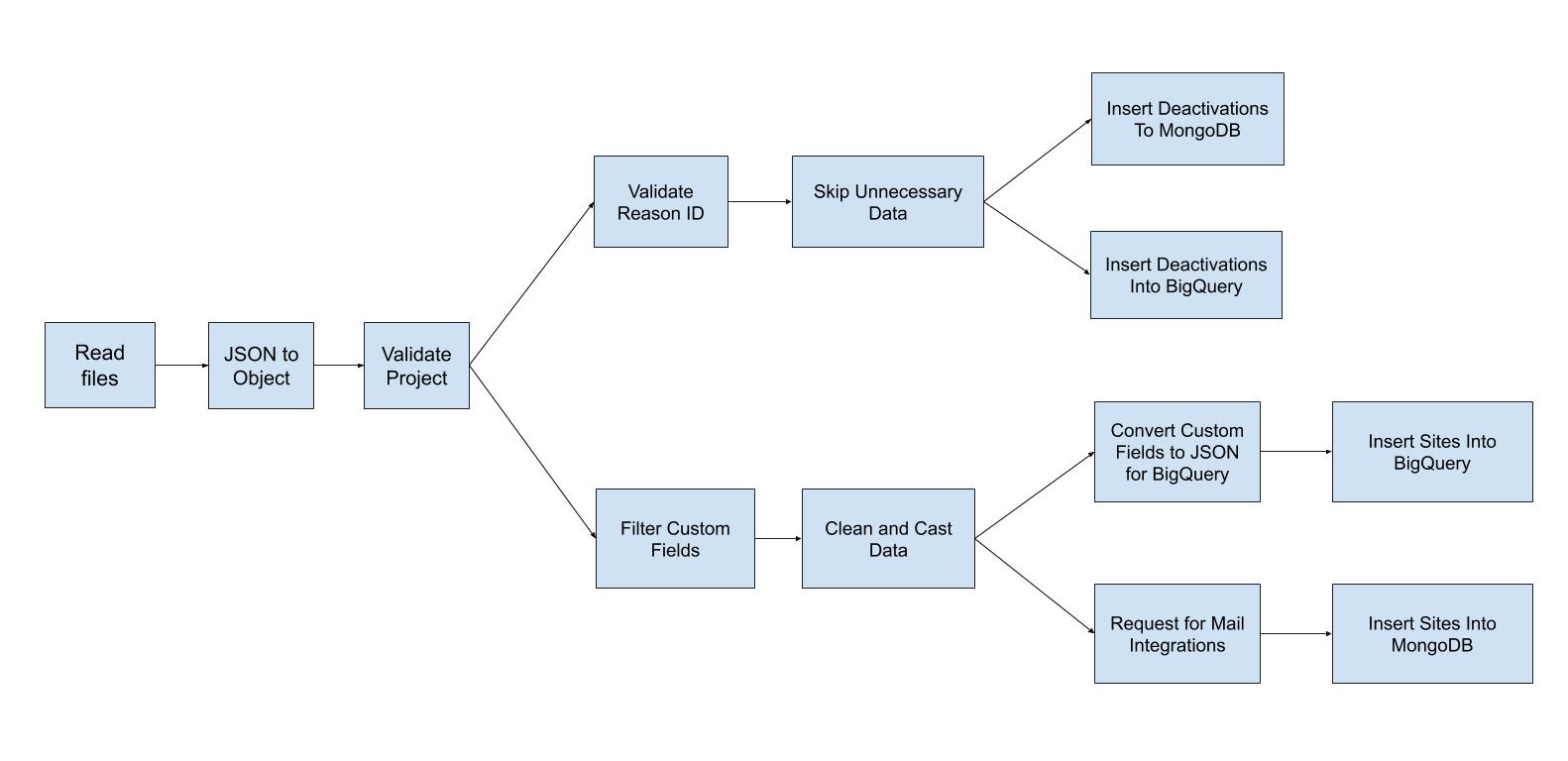
There are mainly 13 steps on this pipeline. The task of every step is as follows.
Read Files:
Read all JSON files of the previous hour from GCP cloud storage.
JSON to Object:
This step just converts JSON to a Python dictionary for further execution.
Validate Projects:
This step checks the hash, is the hash of a valid project or not. If the data is valid then send it to the next step otherwise skip it.
Filter Custom Fields:
This step validates the custom fields of a project. If it found any valid custom fields then it creates an array of those custom fields. Send the array with other data to the next step.
Clean and Cast Data:
Create a fresh array of data. This step cast data type for the necessary fields and just take the valid fields and skip unnecessary fields. After this step, we get a fresh and clean array of data.
Request for mail integrations:
This checks the project on MongoDB. If the mail integration (MailChimp, MailJet, WeMail) is true then send a request to the appsero-api server for sending the mail to the provider list. If there is no mail integration then it doesn’t send any request.
Insert Sites Into MongoDB:
Insert the site into MongoDB if this is a new site. If the site already exists then it updates all information on the site. MongoDB database is used to store the latest data for each site.
Convert Custom Fields to JSON for BigQuery:
We are storing custom fields as a JSON string in BigQuery. This step converts the custom fields array to JSON string so that this can be inserted into BigQuery.
Insert Sites Into BigQuery:
Insert the site into BigQuery. We are using BigQuery as a data warehouse. We store all historical data of sites into BigQuery.
Validate Reason ID:
This step checks the reason id on MongoDB. Here reason_id is the slug of the deactivation reason. If the reason_id is valid then it sends the data to the next step otherwise skip the data.
Skip Unnecessary Data:
This is step clean data for the deactivation table. This step removes unnecessary fields for the elements.
Store Deactivation to MongoDB:
This step saves the latest deactivation to the MongoDB database. MongoDB database doesn’t contain historical data, deactivation just contains the latest deactivation of a site.
Store Deactivation to BigQuery:
This step saves all deactivations to the BigQuery. BigQuery stores historical data of deactivations.